When it comes to artificial intelligence, the sci-fi scene created in the movie “The Matrix” once caused a sensation in the world and led the trend. Based on the assumption of an American philosopher “brain in a vat”, the film describes the background: humans who thought they lived in the late 20th and early 21st centuries were actually “nurtured” by machines in the “cradle” hundreds of years later. However, the human beings who were “imprisoned” in the “cradle” were “freed” in the world created by the artificial intelligence “Matrix”.
This makes us think again: If your brain is controlled by a machine, sending you various neural electrical signals and giving feedback as before, can you find out?
Neurobehavioral patterns of the human brain
The human nervous system consists of two parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The brain is the largest and most complex structure of the former and the most advanced part of the nervous system. Therefore, in all kinds of science fiction works, the brain is the most critical element. For example, in Liu Cixin’s “Three-Body Problem”: In order to penetrate the interior of the three-body man and minimize the load mass, humans finally decided to send only the brain into space.
Neurons are the most basic structural and functional units of the nervous system. To understand the human brain, we must understand neurons. Below we focus on neurons and how they work.
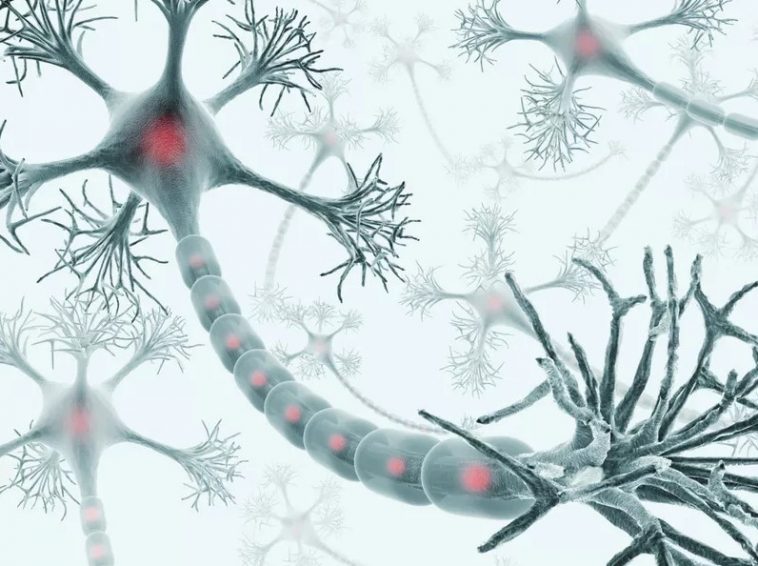
Neurons are the most central elements of neural behavior. There are over 10 billion neurons in our brain. Studies have found that there is a significant positive correlation between the volume of the brain’s gray matter (composed of neuronal cell bodies) and intelligence, so in people’s usual cognition, the more neurons, the smarter the person.

A neuron consists of two parts: the cell body and the process. The protrusions of different lengths carry different functions, the dendrites are shorter for receiving signals, and the axons are longer for transmitting signals. To put it in another way: dendrites are like doors to a neuron, and axons are the knocking hands. When the neuron hears the knock on the door, it opens the door and gets the signal to act, and if the neuron needs to transmit information to others, it knocks on the door of others. Each neuron has many doors and many hands, which means that each neuron is connected to many neurons. Think about it for a while and you’ll see how huge the network of neurons is.
Just as we like our friends who are quick to answer when we chat, neurons also like those who are quick to respond when they send signals. Slow-moving neurons are gradually discarded, making the neuron network more agile and refined. (Perhaps this is why everyone thinks the brain gets smarter the more you use it.
Principles of artificial intelligence
After understanding the processing and transmission of information by the human brain, let’s take a look at the development of artificial intelligence.
The development of artificial intelligence can be described as twists and turns. From the 1950s to the 1980s, it was the era of symbolism. People tried to give logical reasoning capabilities to computer systems by analyzing the way the human brain processes problems, but they were unsuccessful in the end; expert systems became mainstream in the following 20 years. People try to summarize human knowledge and teach it to computer systems, but they also encounter Waterloo; since the 21st century, the importance of data has been gradually realized, and mining information from data has become a trend. Deep learning based on big data has been obtained in the fields of speech and images. Great success. The speech-to-text and automatic translation that we are now familiar with are the first major achievements of this stage.
As the core of current artificial intelligence, it is necessary for us to understand some basic contents of deep learning.
The predecessor of the deep learning model is the neural network, which also shows that the former imitates the neural network of the brain to a certain extent.
What human behaviors cannot be simulated by artificial intelligence?
With the vigorous development of artificial intelligence technology, the sci-fi imagination that was once advanced in movies seems to be coming into reality step by step. The confrontation between the human brain and artificial intelligence is also becoming more and more obvious, especially in the field of games that we are familiar with: Deep Blue (chess AI) and AlphaGo (Go AI) have achieved remarkable achievements in the competition with humans.
We can’t help but ask ourselves, what aspects are humans superior to?
Artificial intelligence based on big data, the more we understand artificial intelligence, the more we recognize the digitization of human behavior. Just imagine, if there is a machine that records all personal information and social data, will there be a difference between humans and machines?
It is difficult to give a definite answer to this point. In particular, the current hardware conditions cannot support such a huge amount of data, and the future is even more difficult to predict.
One of the arguments that “artificial intelligence cannot replace humans” is the boundary nature of artificial intelligence. Once the range is set, the program will only run within a fixed range, and cannot jump out of this frame.
But in all fairness, do we humans have no boundaries? Humans in the past believed that the sky was round and the place was round, and today’s human beings may also be watching the sky in the future. The truth is always within a certain limit, beyond which other conclusions may be drawn.
Another big obstacle for “AI cannot replace humans” is the human emotional realm. The core of artificial intelligence is computing, and everything based on imagination, association, guessing, innovation, etc., in the foreseeable future, artificial intelligence is still difficult to compare with humans.
There are tens of billions of neurons in the human brain, and the complexity of artificial intelligence is far less than this, so its operations are always limited, and its functions are always bounded. AI may never figure out why humans connect two irrelevant things, nor does it know that under the impact of strong emotions, humans will do things that go beyond their own routines and limits.
For now, the line between the creator and the created is still very clear. Perhaps because of this, we will usher in the “smart era” of human-computer interaction and the combination of human brain and artificial intelligence.


GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings