The three payloads of “Kuafu-1” – the full-sun vector magnetic imager (FMG), the solar hard X-ray imager (HXI) and the Lyman Alpha Solar Telescope (LST) are in normal condition, the satellite platform and the functional performance of each payload It meets the design requirements, establishes high-precision stable attitude pointing, stable working temperature environment, reliable satellite-ground measurement and control and data transmission links, and obtains stable energy, which effectively guarantees the satellite to carry out work in orbit.
According to the established plan, a large number of on-orbit tests and observations of the sun have been carried out. Among them, the full sun vector magnetic imager (FMG) has carried out solar magnetic field observations in space for the first time, and the quality of the obtained partial longitudinal magnetic maps of the sun has reached the international advanced level. It has laid a good foundation for focusing on the scientific goal of “one magnetic storm and two storms” and realizing high-time resolution and high-precision observation of the solar magnetic field.
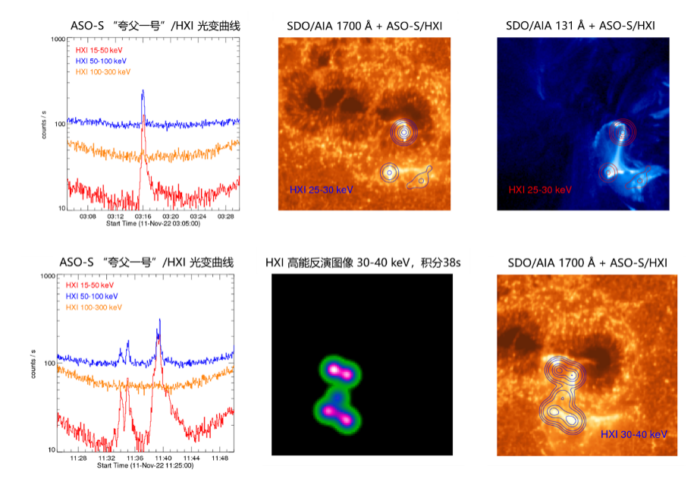
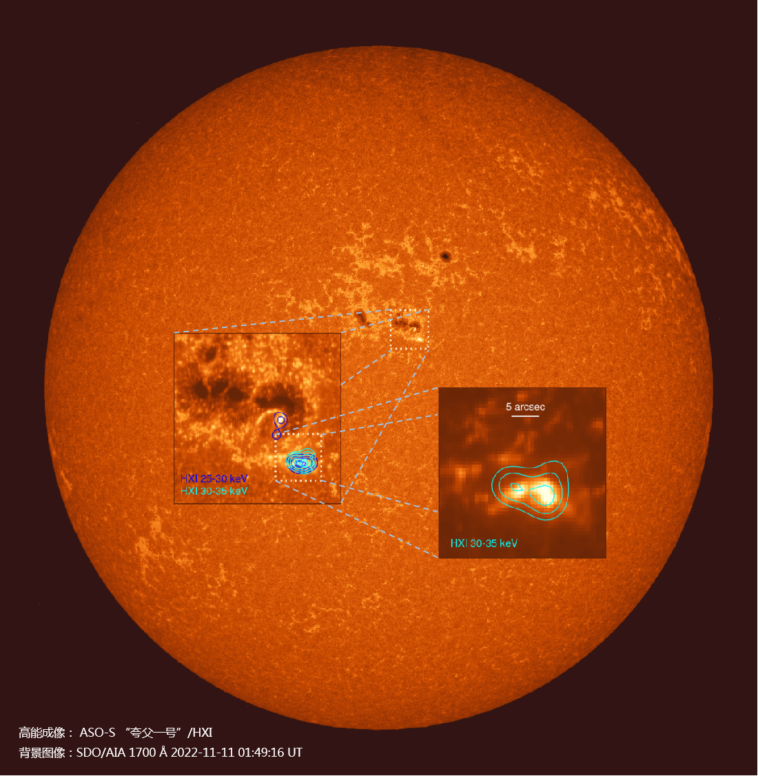
One of the three sub-payloads of the Lyman Alpha Solar Telescope (LST), the Solar Surface Imager (SDI) obtained the Lyman Alpha band full-surface image of the sun on the satellite platform for the first time in the world, and the image of the evolution of the prominence is clear and complete. Another sub-payload – the Solar White Light Telescope (WST) observed 2 rare “white light flares” on the edge of the sun, and the observation capability of the Lyman Alpha band has been verified. With the sub-load – the solar coronagraph (SCI) starting to observe the coronal mass ejection, the Lyman Alpha Solar Telescope (LST) will play an irreplaceable role in the formation of the solar surface of the coronal mass ejection and the observation of the near coronal propagation.
In the next stage, “Kuafu-1” will carry out and complete the on-orbit test according to the established plan, and transfer to the on-orbit scientific operation stage as soon as possible. At the same time, “Kuafu-1” will give full play to the combined observation characteristics of the three payloads, strengthen internal and external cooperation and open data sharing, and realize the scientific goal of “one magnetic storm and two storms” as soon as possible
The full name of “Kuafu-1” is “Advanced Space-based Solar Observatory” (ASO-S). It is another space science satellite developed and launched by the Chinese Academy of Sciences Space Science Phase II pilot project. The launch center successfully launched the Long March 2D carrier rocket. The scientific goal of the “Kuafu-1” satellite is aimed at “one magnetic storm and two storms”, that is, to simultaneously observe the solar magnetic field and the two most violent eruptions on the sun – flares and coronal mass ejections, and study their formation, evolution and interaction and each other, while providing support for space weather forecasting.
The National Space Science Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences is responsible for the development and construction of the overall project and the ground support system for the “Kuafu-1” satellite project. The Institute of Microsatellite Innovation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Astronomical Observatory, the Zijin Mountain Observatory, and the Changchun Institute of Optics and Mechanics are respectively responsible for the satellite platform and three satellites. The research and development of the platform payload, the scientific application system is in charge of the Purple Mountain Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the measurement and control system is implemented by the Xi’an Satellite Measurement and Control Center of China, and the launch vehicle is developed and produced by the Eighth Research Institute of China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation.



GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings