The enormity of the universe is always daunting, and whenever humans think about their place in the universe, they often find their own insignificance.
No matter how long the history of human civilization is or how powerful technological innovation is, everything is worthless in the universe.
Because it transcends all our cognition, time and space seem to be non-existent here, and matter and desire also become nihilistic here.
Today, human beings use their own technology and knowledge to spy on the mysteries of the universe. Although our lifespan is very limited, it still does not prevent us from further observation.
A galaxy about 60 million light-years from Earth
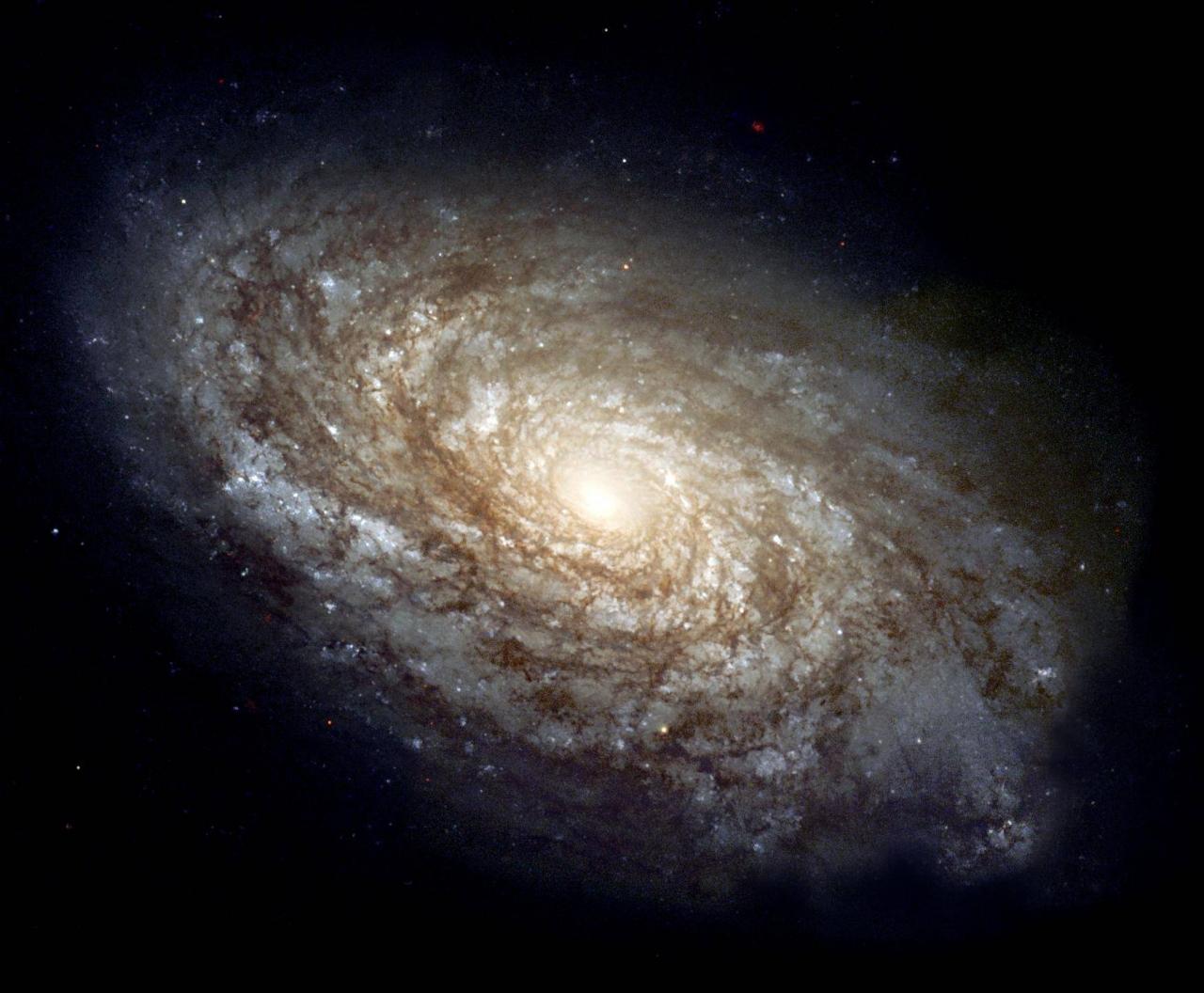

Our Milky Way is one of many galaxies.
It is composed of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust and dark matter, many of which are linked together under the action of gravity.
And the Milky Way itself is not alone. Around it, there are Andromeda, the Large Magellanic Cloud, the Small Magellanic Cloud, and the Triangulum Galaxy.
Why are humans always eager to study everything in the galaxy?

Because it is critical to our understanding of the development of the entire universe and galaxies, scientists can use gravitational analysis and radiation measurements to deduce how the universe is changing, and possibly the future.
Many times we can see in images from space telescopes vast and spectacular galaxies and nebulae quietly docked anywhere in the universe.
But they are not static, and even galaxies interact with each other, just like other celestial bodies in the solar system.
Galactic fusion could look like this
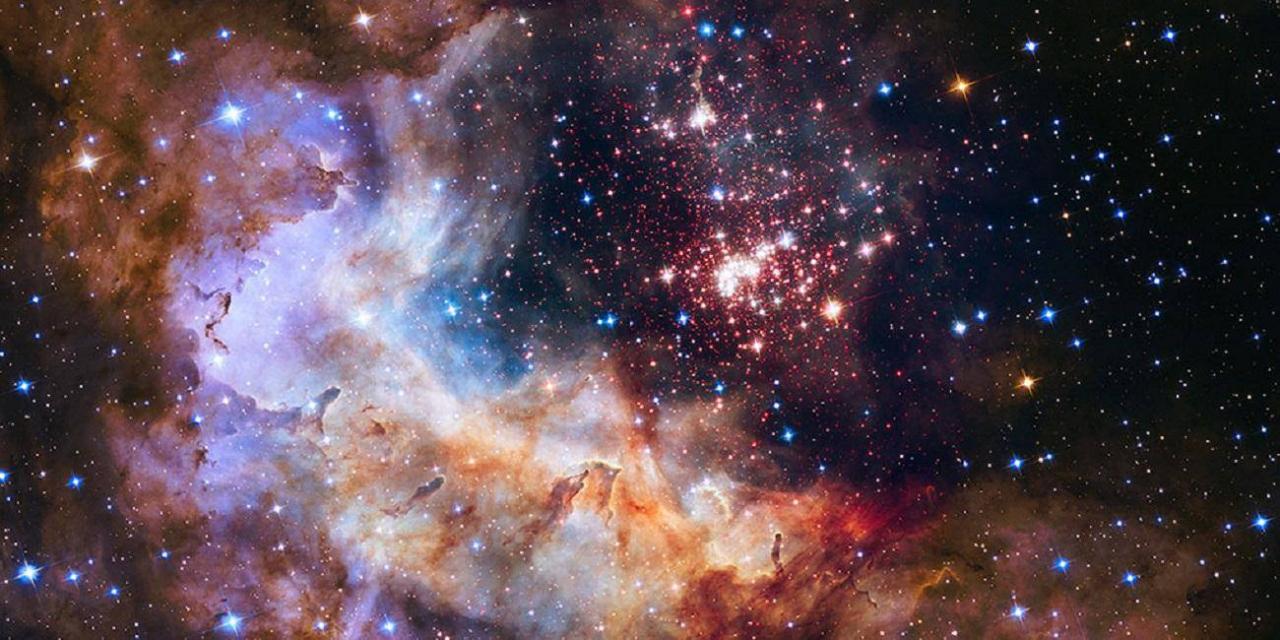

The interactions between galaxies are the result of tiny quantum fluctuations brought on by the Big Bang after the early universe formed.
The evolution and development of galaxies is inseparable from the initial movement, of course, the most important thing is the tidal interaction between galaxies.
Activity between galaxies can bring changes to galaxies, and some near misses can cause them to warp and cause some exchange of gas and dust.
A collision occurs when two galaxies pass directly through each other and have enough relative momentum not to merge.
galaxies classified by Hubble
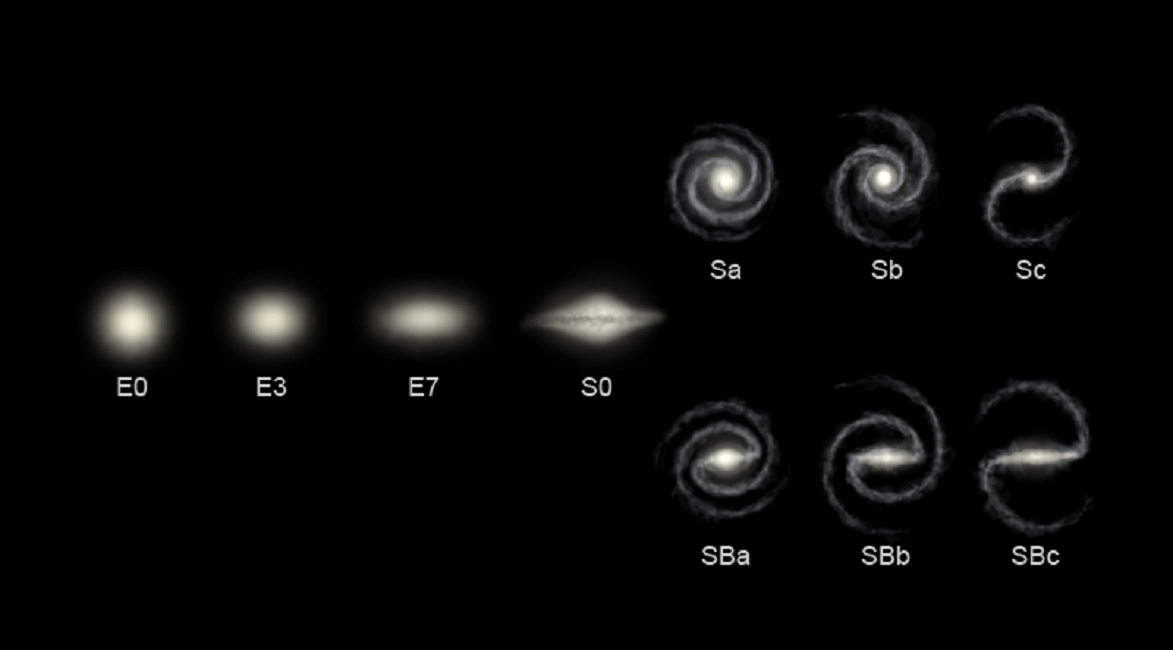
But stars within interacting galaxies usually don’t collide, and the gas and dust in both forms interact.
Sometimes stars are created in this way, and star systems within galaxies are more distant from each other than we think.
For galaxies, after fusion, they change their shape again.
layers of galaxies
The evolution of galaxies in the universe is usually measured in billions of years, and the time span is very long.
On larger structural scales, galaxy clusters and superclusters, which are more spectacular than galaxies, appear even more bizarre.
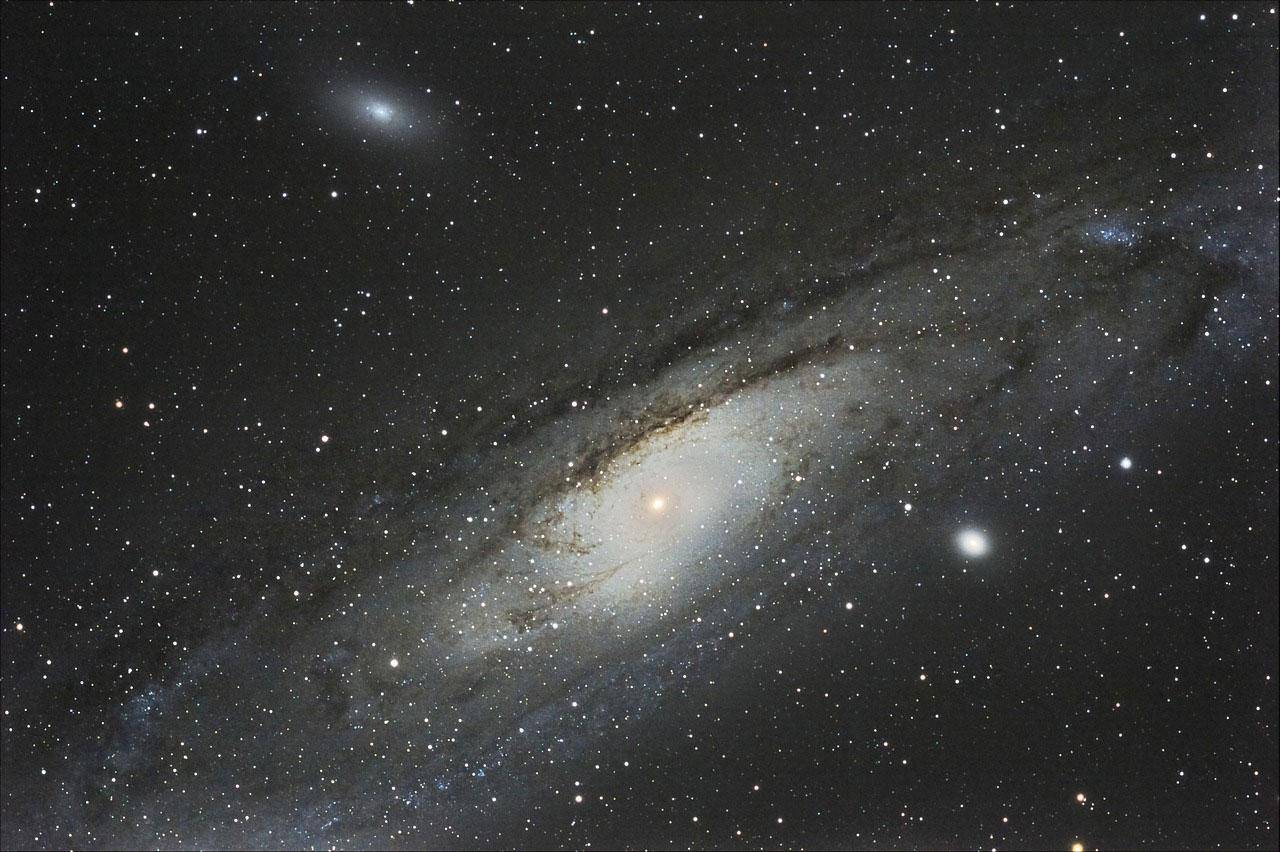
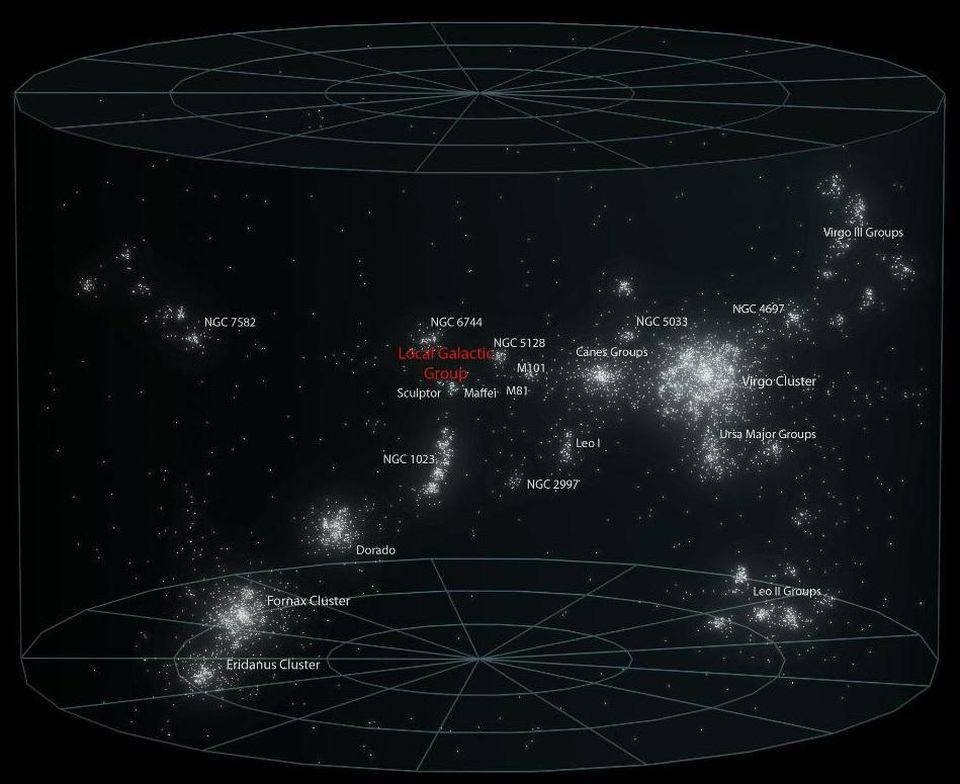
Leaving the Milky Way is the Local Group of Galaxies. There are about 50 galaxies here. The largest is Andromeda, followed by our Milky Way.
Galaxies in the Local Group span an area about 10 million light-years across, but that’s still not all of us.
Andromeda Galaxy

The Virgo Supercluster is a larger cosmic structure above the local galaxy.
It itself contains galaxies in the Virgo Cluster and the Local Group of galaxies, and scientists speculate that there are at least 100 groups and clusters within its 110 million light-year diameter.
This is one of about 10 million superclusters in the observable universe, and is located in the Pisces-Cetus supercluster complex, part of a galactic filament.
When we look here, the Milky Way appears so small, its internal structure and the span of space transcend time itself, and time seems meaningless here.
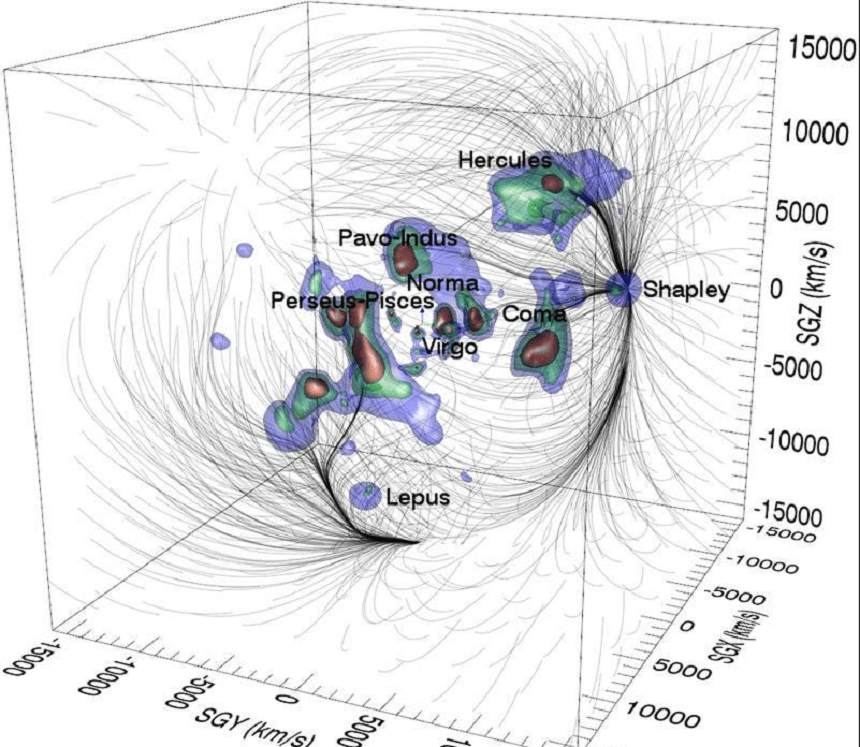
Map of the Laniakea Supercluster and its constituent galaxy clusters

And this is still not the universe. Above Virgo, the Laniakea supercluster is the owner of it all.
Laniakea means “open sky” in Hawaiian.
Its discovery came from Richard Brent Tully of the University of Hawaii, as well as numerous astronomical institutes such as the University of Lyon and the Hebrew University.
The Laniakea Supercluster contains about 100,000 galaxies, extends over 520 million light-years, is 100,000 times the size of the Milky Way, and consists of four parts.
In addition to the Virgo Supercluster, there are the Hydra-Centaurus Supercluster, the Peacock-Indus Supercluster, and the Southern Supercluster.
Visualization of Raniakea
Scientists have been studying the gravitational structure of the universe for the past few decades, and astronomers believe that our own Milky Way should lie on the edge of a local supercluster of galaxies.
It is within a structure about 100 million light-years wide at the center of the Virgo cluster of galaxies.
Earlier observations by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey showed that astronomers had seen larger structures in the universe, measuring hundreds of millions of light-years in size.
By calculating the redshift of galaxies in the universe, scientists were able to calculate 3D models of them.
Galaxies observed by the Sloan Sky Survey
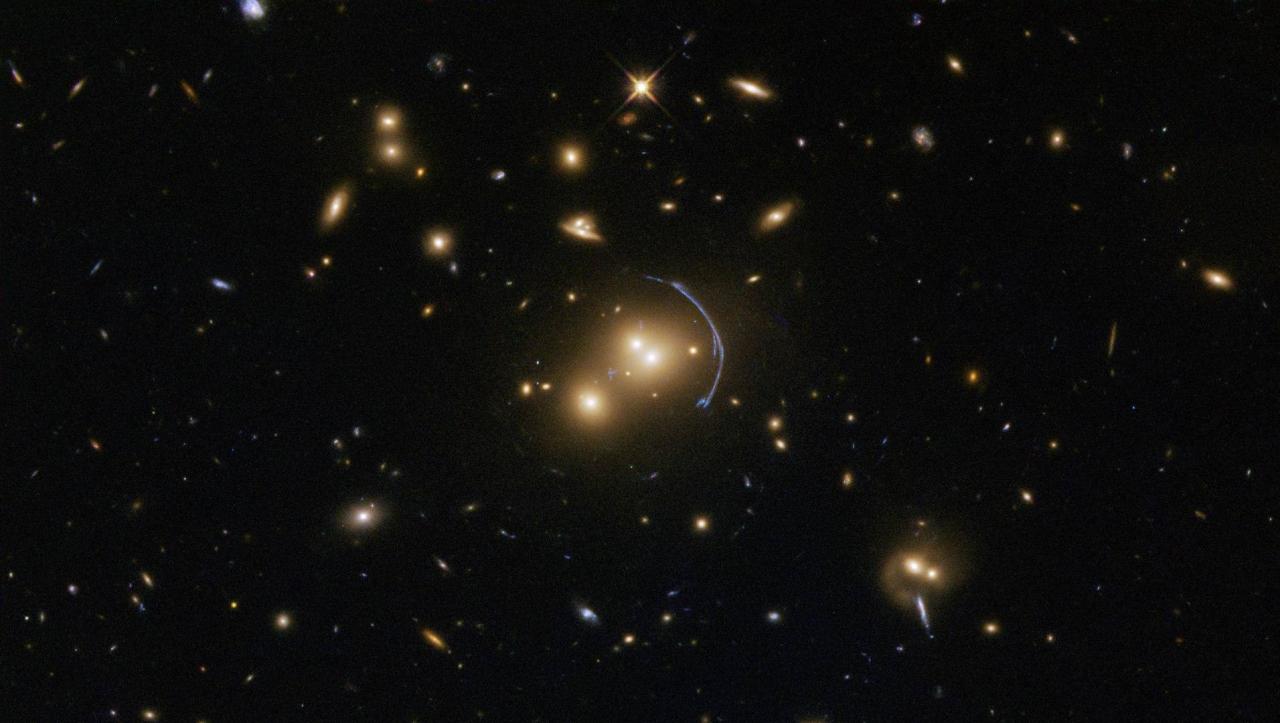

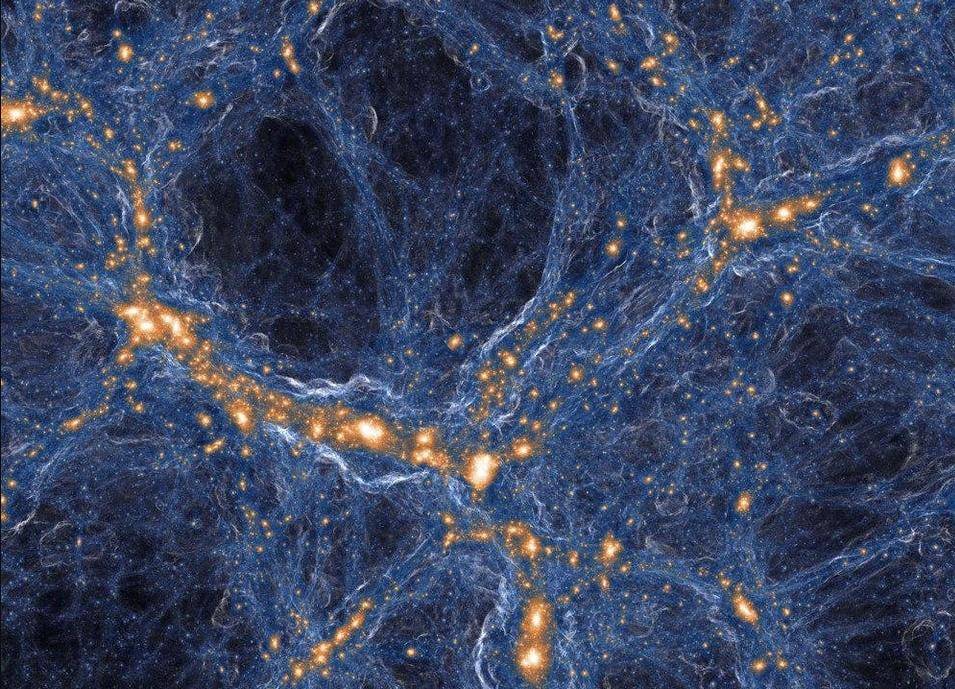
At the largest scales, the universe looks like a vast web of stars connecting galaxies and galaxies clustered with groups of galaxies.
Many combined groups form galaxy clusters, and galaxy clusters merge to form larger galaxy clusters.
The largest scales that can be observed today are superclusters, and scientists at the University of Hawaii have taken a different approach to understanding them.
For example, the special velocity of galaxies, which is the motion of galaxies due to their own gravity.
The growth of the cosmic web and large-scale structure in the universe
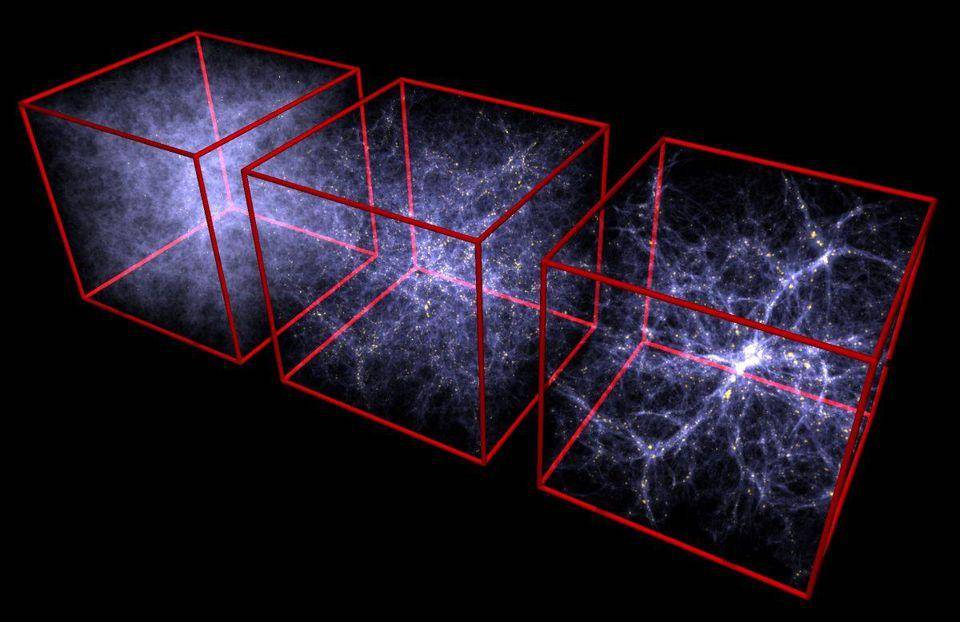
In this motion, the galaxies are moving away from each other, and the Milky Way, including a large number of other galaxies, is moving toward the cosmic giant attractor.
It is located 160 million light-years away in a dense region near the Centaurus, Norma and Hydra star clusters.
under the universe
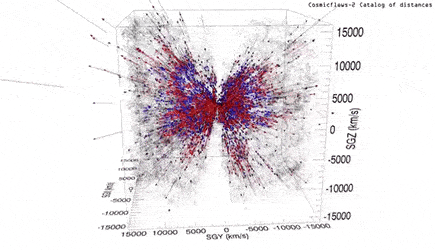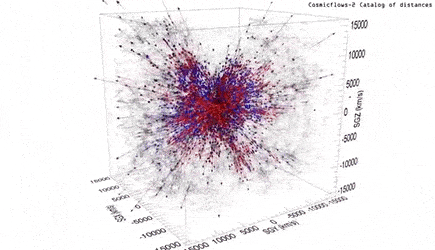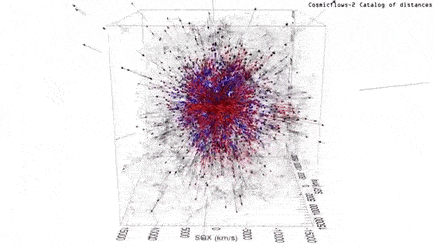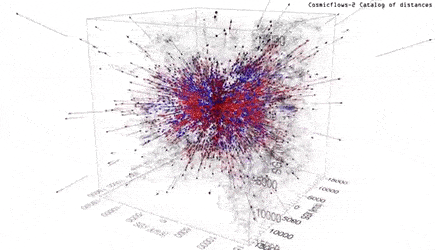
In order to understand the location of superclusters, the team led by Professor Tully mapped the motion of galaxies to infer the gravitational landscape of the local universe and redrawn the map.
Where the Milky Way is

To calculate this, the team used a database-2 (Cosmic Stream-2), a compilation of distances and particular velocities for more than 8,000 galaxies.
The numerical aspects mainly come from the luminosity-linewidth correlation of the spiral, the Tully-Fisher relationship (the empirical relationship between the mass or intrinsic luminosity of a spiral galaxy and its asymptotic rotation speed, or the width of the emission line), etc.
Using these data and subtracting the average rate at which the universe is expanding, the scientists got the results.
This method is superior to just mapping the location of matter because it allows scientists to map uncharted regions of the universe.
From an observational perspective, it relies on the influence of galaxies rather than direct observations.
In addition, the motion of galaxies reflects the distribution of all matter.
Without accounting for the expansion of the universe, the Hawaiian science team has shown streamlines that wriggle under the influence of gravity in other regions.
Based on this motion, Tully’s team defined the edge of a supercluster as the boundary where these streamlines diverge.
On one side of this line, galaxies flow toward the center of gravity, and then across it to the other.
The whole thing looks like the watershed on the watershed flows to the left of the highlands, or to the right.
Lania Kea’s “Fluid” Model
Correlation analysis has also revealed other structures in superclusters, including a separate supercluster in the constellation Perseus-Pisces, and a distant concentration called Shapley.
Its location is about 650 million light-years away, and Raniakea is moving towards it.
The structural analysis of Rania comes from existing data, scientists at the Tartu Observatory in Estonia believe:
It may change in the future as Raniakea is further observed, and the exact boundaries of Raniakea are not so clear today.
Identified galaxies shown here, circled by white dots
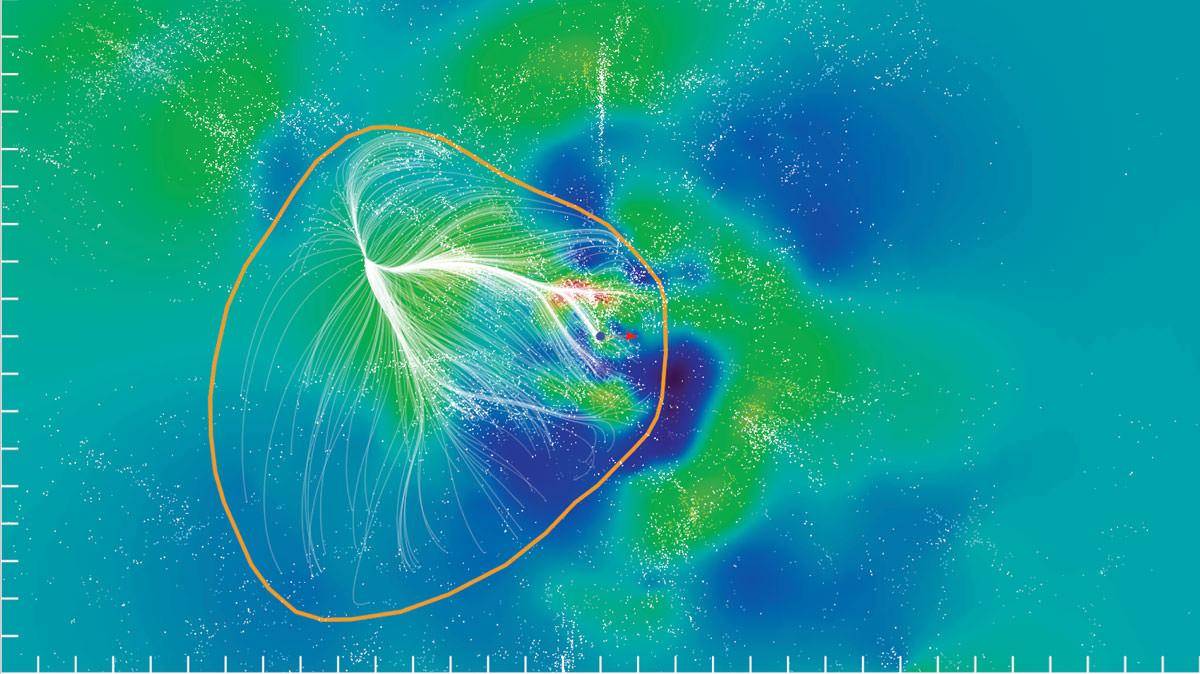
Because the measured distances on which the special velocity calculations rely are rare at 300 million light-years away, scientists have had a hard time figuring out what’s going on there.
And Tully said something interesting:
“Now that Raniakea is heading towards Shapley, our supercluster might just be the trunk of an elephant.”
At present, the team led by Tully has divided a “local regional gravitational basin” based on the research of Lania Kea, and whether it is an appendage of a larger object still needs accurate measurement data. This distance is in the current data catalog. 3 times.
Outlined in light blue is a huge collection of galaxies
Now that we look back at the structure of entire galaxies and galaxy clusters in the universe, it’s no surprise that large-scale structures like Laniakea are scary.
All galaxies are the product of gravitational activity, and the changes brought about by the expansion of the universe ended 6 billion years ago.
Today, dark energy dominates the universe.
According to the theory of cosmic inflation, gravity has not yet completely bound the development of the entire universe.
In the future, the galaxies will become more and more sparse due to the Great Expansion, the star cluster in which the Milky Way is located will not merge with the Virgo cluster, and the cosmic filament structure will appear more hollow.
Laniakea is included in the larger scale structure
And the activities of the past are the existence of today, and the changes of today are the performance of the future.
In the following billions of years, they spread farther from each other, and finally “disappeared” in the universe, which is also destined to be the tearing ending brought about by the great expansion of the universe.



GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings