Astronomers discovered the burial of the “Hades” of the Galaxy -“Dead Star“. The so -called “Dead Star” is the kernel wreckage of the star. Here is the remains of large -quality stars, including black holes and neutron stars. They are scattered around the galaxy, but the overall structure of the body is more large and fluffy than the galaxy body.
Millions of stars constitute the body of the Galaxy, but once they die, the situation will change. Large -quality stars will end their lives in the tragic supernova. The outbreak of the supernova will throw away the shell of the star to tighten the core of the star. The huge shock wave will also accelerate the residual star core to the inter -galaxy space that is enough to fly to the vast galaxy.
It can be seen that the distribution characteristics of dead stars must be different from ordinary stars.
Since the birth of the Milky Way, at least billions of dead stars have been produced. But astronomers who like counting stars are very few dead stars. This time, researchers at the Astronomical Research Institute of the University of Sydney, with extremely patience and enthusiasm, recovered the life cycle of these ancient dead stars, and drawn the first detailed 3D distribution map of the galaxy dead star in human history.
It is extremely difficult to draw such a star map. The most difficult thing is that you can’t find the dead star. The black holes and neutron stars that were just died may still be near the place, but those old ones did not know where to fly.
The asymmetric shock wave generated by the supernova eruption will accelerate them to millions of kilometers per hour in the random direction. Therefore, the location of the dead star is often not where their predecessor is. And in space that has almost no resistance, once the speed is obtained, it will never stop. After billions of years passed, everything changed. Those ancient black holes and neutron stars have become ghosts flying in the interstellar space.
In order to understand the distribution of dead stars in the galaxy, researchers have built a complex model. In this model, enter the information related to the location of the key nodes of the star evolution period to get a distributed map of a dead star of the galaxy.
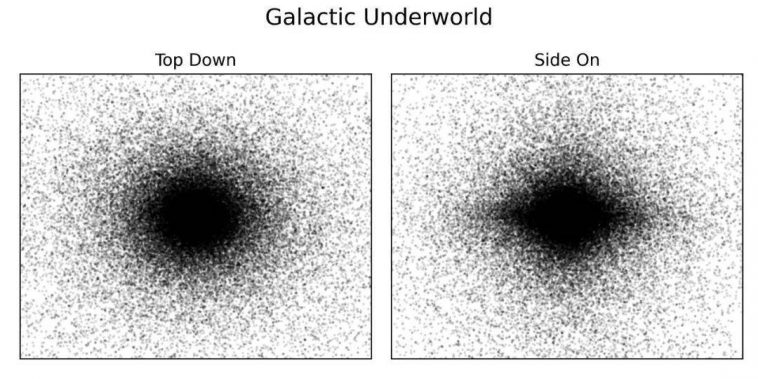
Judging from the preliminary results, a dead galaxy is much larger and more fluffy than a living galaxy.
From the side, the thickness of the galaxy “Hades” is three times that of the galaxy body; if you look down, we will find that it loses the iconic arms of the galaxy. Over time, the kinetic energy of the supernova burst on the dead star was erased, and this feature was erased. Most of the dead stars flying around each other entered the silver halo, and at least one -third of the galaxy was left to enter the vast galaxy space.
What surprised researchers was that Dead Star would be close to the solar system. From a statistical point of view, the nearest dead star is about 65 light years away from the solar system. In astronomical semantics, this is quite close.
Our sun will eventually die, but the remains of the sun are a “white dwarf”, which is the same as the density of the remains of large -quality stars. The sun does not get the acceleration of the shock waves of the supernova. So be sure that the sun cannot enter the “Mingfu” of the Milky Way.



GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings