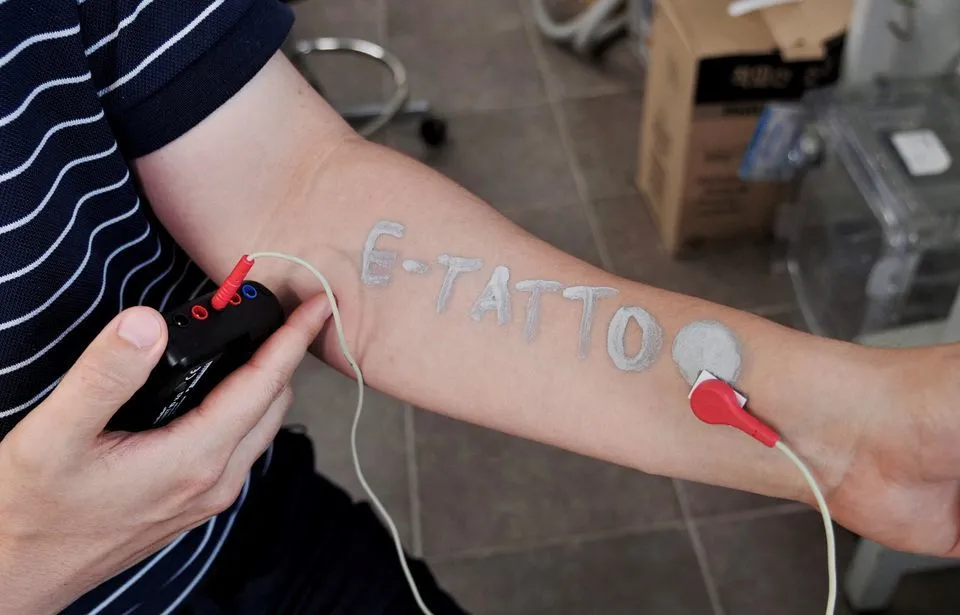
The ink used in tattoos is made of gallium particles, which are harmless to the human body. Gallium is a soft, silvery metal often used to make semiconductors or thermometers. Platinum-decorated carbon nanotubes help conduct electricity while enhancing durability. “When it’s applied to human skin, the tattoo won’t fall off even when rubbed,” said project leader Steve.
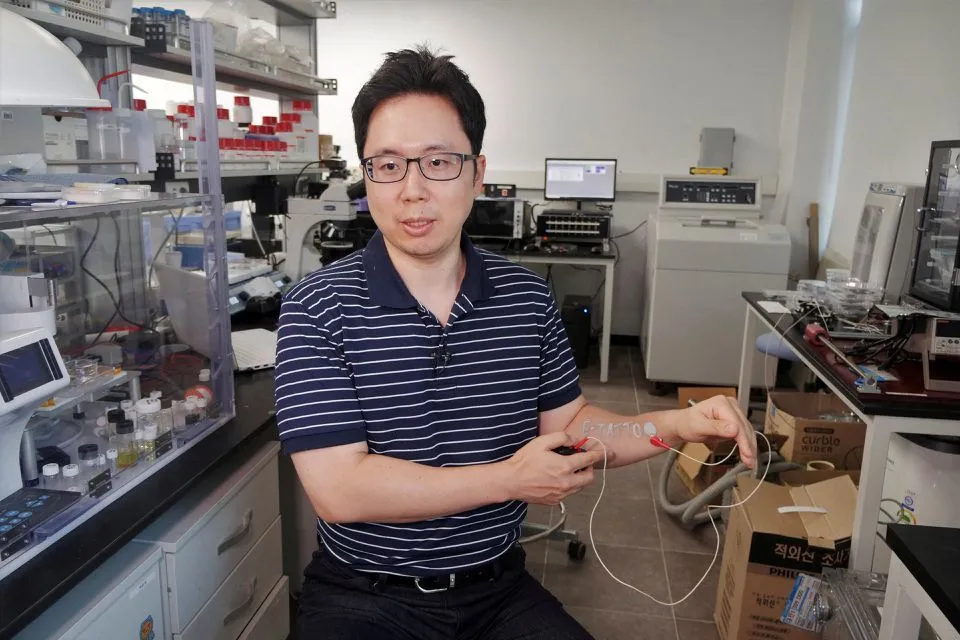
Steve Park, Professor of Materials Science and Engineering
The electronic tattoo ink connects to an electrocardiogram device or other biosensor, sending the patient’s heart rate and other vital signs, such as glucose and lactate data, to a monitor. The researchers’ ultimate goal is to have “tattoos” replace biosensors.


GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings