Do you know what day is today?
Twenty-eight years ago, Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 fell into Jupiter’s atmosphere at a speed of 210,000 kilometers per hour, forming the astronomical spectacle of “comet-wood collision”. They created a series of explosions over the course of a week, the largest being the equivalent of 600 million tons of TNT or 100,000 hydrogen bombs.
Although astronomers are looking forward to seeing such a spectacular sight on a clear night, people can’t help but worry –
This time it is Jupiter, but will the next impact target of “extraterrestrial visitors” such as comets or asteroids be the Earth?
Let’s talk about this today!
01
Thanks to the asteroid “The Grace of Not Killing”
The so-called “near-Earth asteroids” are asteroids whose orbits intersect with the Earth’s orbit, or may intersect the Earth’s orbit after being perturbed by the planet’s gravitational force in the future.
You must know that there are neither traffic lights, traffic police, nor switchmen in the solar system. These asteroids intersect with the orbit of the earth, and there is a danger of hitting the earth. (For the sake of simplicity, when we talk about “asteroids” and “small celestial bodies”, we also include the nucleus of comets. After all, it is similar to “asteroids” in terms of damage to the Earth.)
Small objects in the main asteroid belt are marked brown
NEOs are marked in cyan
Earth’s orbit is off-white, the third circle from the inside to the outside
Some friends may think that the universe is so big and the asteroid is so small, the possibility of hitting the earth must be very small, right?
But the opposite is true.
For example, everyone has been in a car, and they must have experienced the scene of raindrops crackling on the car window on a heavy rainy day. If the earth is a car, in the driveway that revolves around the sun, the window glass of the earth will continue to crackle. Noisy, but it wasn’t raindrops that hit.

It is estimated that 25 million large and small meteoroids break into the earth’s atmosphere every day, and the cumulative total is about 15,000 tons per year.
The reason we can still read this article with our phones steady is because, fortunately, most meteoroids are very small. The vast majority of meteors that can be seen are caused by small objects the size of sand or mung bean, and their sparrow tactics usually do not have serious consequences.
However, “meteoroid” and “asteroid” are just human classification terms, and there is no clear line between them. If a “meteoroid” grows big enough, it may hit the lower atmosphere or even the ground, causing major disasters. Here are some of the more famous ones:
In the early morning of February 15, 2013, a bolide streaked over Chelyabinsk, Russia. The light overwhelmed the rising sun. The bolide left a trail of smoke and dust about 10 kilometers long in the sky. , The meteorite that was not burnt in the air smashed a 6-meter-wide hole on the frozen Chebakur Lake. More than 7,200 houses were damaged by the blast shock wave, and 1,491 people were injured indirectly. It is estimated that the bolide event in Chelyabinsk was caused by an asteroid with a diameter of 17 to 20 meters.
Historically, larger-scale celestial impacts are not far off.
On June 30, 1908, in Russia, an earth-shattering explosion occurred near the Tunguska River. The shock wave shattered window glass within a radius of 650 kilometers, and 80 million trees over 2,150 square kilometers were burned and fell down. , barometric pressure recorders as far away as the UK have detected pressure fluctuations from the explosion. The scientific community now generally believes that the perpetrator of the Tunguska explosion was a stony asteroid with a diameter of about 65 meters.

The most famous asteroid impact site is probably the Chicxulub crater in Mexico. About 66 million years ago, an asteroid with a diameter of at least 10 kilometers hit here at a speed of 20 kilometers per second. It opened the prelude to the Cretaceous extinction event. 75% of the species on earth, including all non-bird dinosaurs, bid farewell to the big stage of life on earth forever in this extinction event.
So from this point of view, human beings can develop to the present, and they may really have to thank asteroids for their “grace of not killing”.
02
How powerful is the impact
I’m afraid you can’t write a line
As mentioned earlier, a 10-kilometer-scale asteroid caused a mass extinction. You may wonder: a stone only 10 kilometers in size, which is the size of a city, can actually destroy the Daqian world with a surface area of 500 million square kilometers. ?

Don’t forget that this rock is still 10 kilometers high – more than a thousand meters higher than Mount Everest. Such a giant mountain hits the ground at high speed, we can use the kinetic energy formula to calculate the energy it carries (the process of combining the formula is omitted):
This energy ≈ density×diameter³×velocity²÷3.82
Fill in the data one by one into the formula, all according to the standard units of the International System of Units. The average density of carbonaceous chondrites is 3300 kg/m3, the diameter is 10000 meters, and the speed is 20000 meters/second.
As you will see, this formula calculates the product of the square cubes of various thousands of ah, and the final result is about 346,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 joules – the top three estimates by the scientific community for this impact are 420 , but of the same magnitude, it is a 24-digit number (you can see that ↓↓↓ is not written on a line).
420,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 Joules
What is this concept? It is equivalent to all the energy produced by the core of the sun every millisecond, or the energy released by the explosion of 2 million Tsar hydrogen bombs. If the surface of the earth’s 500 million square kilometers is uniformly covered with water at a depth of 2 meters and 0°C, then this energy is sufficient. Boil all this water.
Fortunately, the energy of the impact at that moment will be concentrated at the impact point, which will completely vaporize the asteroid and collapse a huge crater 100 kilometers wide and 30 kilometers deep on the spot, instead of flattening all the energy at once. spread over the entire earth. But don’t be too happy, the law of conservation of energy determines that it is only a matter of time for everyone to receive a boxed lunch, because the impact of the impact is late but arriving…
Starting from the impact point, there are strong winds with a speed of 1,000 kilometers per hour, and a tsunami with a wave height of 1,500 meters. In addition, 25 trillion tons of matter will be thrown high into the sky in an instant, some of which will be splashed into space and never come back, and some of them will fall back to Earth, and they will re-ignite when they re-enter the atmosphere, A firestorm will sweep the world.

A large amount of dust and ashes caused by the impact are suspended in the atmosphere, blocking sunlight for a long time, hindering the photosynthesis of plants, and the ecosystem collapses. Consumers at all levels of the food chain will perish one after another.
Come this way, the earth has been abused like this, will it be peaceful in the future? The attitude of the asteroid is naturally:
I was wrong, I will dare next time.
03
Humans must not only rely on asteroids “grace not to kill”
Although no asteroid has really dealt a fatal blow to mankind yet, we really can’t bet luck on this matter.
According to NASA estimates, about every 5,000 years, an asteroid over 140 meters in size will collide with the Earth. On July 25, 2019, an asteroid tentatively numbered 2019 OK flew by at a distance of 72,000 kilometers from the earth, which is less than one-fifth of the distance between the earth and the moon. Is it scary enough to be so close? What’s even more terrifying is that it was not discovered by humans until the day before the flyby!
On April 13, 2029, the asteroid 99942, also known as the “Destroyer Star”, with a size of 170-450 meters, will fly by about 32,000 kilometers from the surface, which is already lower than the orbit of a synchronous satellite. !
Humans pride themselves on being intelligent creatures, but if faced with a critical attack from an asteroid, they would die as helplessly as dinosaurs who didn’t read books.
If you want to prevent being inexplicably smeared by asteroids, you must first know how many they are and where they are hiding, and the sooner you find them, the better. Since nearly 30 years ago, a number of NEO monitoring projects have been launched one after another, with an average of 40 small objects being discovered every week, which has been fruitful.
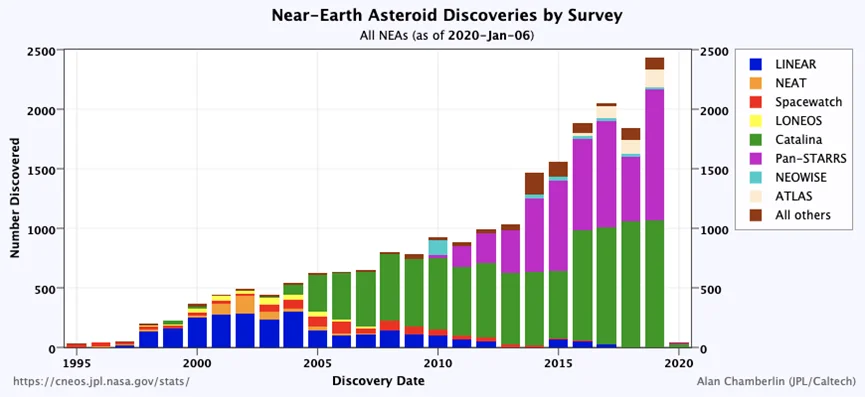
Year-by-year discoveries of various NEO monitoring projects
Why establish a ground-based and space-monitoring system? Isn’t observing from the ground enough? Not enough. Some asteroids came under the cover of the light of bright celestial bodies, such as the one in Chelyabinsk, which flew from the direction of the sun. If you want to find it in advance, you have to look at the stars during the day. Arrival, no one knew beforehand.
Another example is the 2019 OK (the asteroid number mentioned above), which is very bad. In the days when it should have been seen, it encountered a full moon. If the monitoring system is launched out of the atmosphere, then the bright disk of the sun and the moon is next to the dark space, and “finding stars during the day” can also be done.
So, if we’re lucky — or rather unlucky — and do find an asteroid that’s going to hit Earth, how are we going to fix it?
04
To survive or to perish?
Never go gentle into that good night!
Hollywood sci-fi disaster blockbusters love to use asteroids hitting the earth. For example, “The Clash of Heaven and Earth” and “Peerless Catastrophe” have plots where humans try to blow up asteroids. The same is true in reality. In the face of the crisis of destruction, human beings will never sit still. The good news is that there are already many feasible solutions.
Once it is found that an asteroid threatens the earth, all possible solutions can be divided into two categories in the final analysis: disintegration and push away.
Disintegration is the splitting of asteroids into individual pieces (mainly by blasting), small celestial fragments that fly in multiple directions and miss Earth, or are small enough to burn up in the atmosphere.
Pushing away is to derail the asteroid as a whole, or let it accelerate or decelerate, and reach the appointment point ahead or lag, which also achieves the effect of missing the target. The equatorial diameter of the earth is 12,756 kilometers, and the revolution speed is 30 kilometers per second. It takes 425 seconds to complete one body length, which is about seven and a half minutes. The purpose of pushing away is to gain 425 seconds for the earth.
In terms of specific implementation methods, there are the following:
The most easily thought of are thermonuclear weapons. The large amount of thermal energy produced by thermonuclear weapons can locally gasify the asteroid and use this temporarily produced gas to shatter the asteroid, or eject material to push the main body out of orbit. But be careful, once the plan fails, it will not only hit the earth with an asteroid, but also an asteroid with its own nuclear pollution.
A cold-weapon approach, where an impactor can be launched to hit an asteroid, changing its speed or direction. Or use a non-contact method to let a tractor fly with the asteroid, and the gravitational force will gradually pull the asteroid away from its orbit. Hope for a planetary miss.
There are also many niche ideas, such as sending an excavation projectile to the surface of the asteroid, and constantly throwing the material on the surface of the asteroid into space, while it slowly disintegrates, while letting the law of conservation of momentum help change the orbit of the asteroid . Or use lasers or focusing mirrors to vaporize localized surfaces of the asteroid so that it is gradually pushed away by the ejected rocky gas. And so on, and so on.
In terms of effective time, it can also be divided into two categories: blitz and protracted warfare.
Thermonuclear weapons or impactors are blitzkrieg battles, while gravitational traction, excavation projectiles, and partial jets are protracted battles. But no matter which method, it needs to be discovered in time and arranged as soon as possible. NASA’s current most optimistic estimate is a five- to 10-year preparation period, and the impact experiment on the Didymos asteroid 65803 is underway, with the impact expected to be completed in late September/early October 2022.
Finally, let me say something that everyone likes to hear and hear. Although when it comes to small celestial bodies hitting the earth, everyone tends to think in the direction of “natural disasters”, but occasionally some people become very rich because of this (of course, don’t be on the scene when they collide…).
For example, in Germany, there is a small town called Nordlingen, with a population of less than 20,000, located in a huge pit with a diameter of 25 kilometers and a depth of about 100 to 150 meters. At first scientists thought the crater was a crater, but later found coesite, which can only be formed under high-speed impact, indicating that it was an impact crater formed by an asteroid with a diameter of 1,500 meters 15 million years ago.
The impact and high temperature formed an estimated total of 72,000 tons of impact diamonds. Unfortunately, these diamonds were very finely divided, the largest being no more than 0.2 mm. They were mixed in the soil and were inadvertently used by the city’s builders to build roads, build walls and build houses. Therefore, in terms of “diamond content”, this town is really rich in the soil.



GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings