
In all kinds of space launch activities, it can increase the sources of space junk, which generally include the debris of launching rockets at all levels, the debris of spacecraft that failed to launch, satellites that have exceeded their service life and have been scrapped, etc., and the debris in the process of movement. Smaller fragments produced by collisions, explosions, etc.
Since these debris bodies generally “inherit” the initial speed of the previous rocket or revolve around the earth, they will continue to move at a different speed and direction relative to the earth at a certain height. Due to the lack of energy injection, the operation of these space debris The orbit will continue to decay, that is, the distance from the ground will gradually decrease, and eventually it will re-enter the atmosphere out of control. In this process, most of the space debris will be “burned” due to the violent friction with the air, and only the debris with larger volume, compact structure and smaller initial height from the ground will hit the ground.

Up to now, there are about 5,000 spacecraft orbiting the earth, of which more than 3,000 were launched by the United States, nearly 500 in my country, and about 170 in Russia. Take the United States as an example. In recent years, with the intensive launch of Starlink satellites, the number of satellites has been on a linear upward trend. With the implementation of the second phase of SpaceX’s satellite launch plan, the number of satellites owned by the United States will further increase significantly, while The number of these satellites not being launched into orbit for various reasons, the number of satellites being worn out for too long, and the number of failures has also increased significantly, so that the United States has become the country that produces the largest amount of space junk.
In recent years, there have been many incidents of space debris hitting the ground. However, after the rocket is launched, the trajectory of the rocket will be accurately set, and the landing trajectory of the returned debris will also be accurately measured. Therefore, many space debris landed on the ground. The locations of the wrecks are basically located in inaccessible areas such as oceans or deserts. For example, the landing site of many wrecks will be chosen in a vast ocean uninhabited area in the South Pacific. This area is also known as the “spacecraft graveyard”.
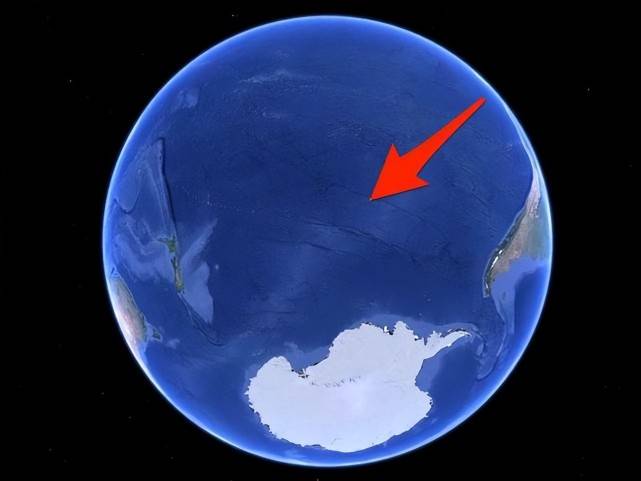
Although space debris will be affected by many uncontrollable factors in the process of falling to the ground, and its trajectory may not completely follow the established route, but basically the errors are within an acceptable range, and it usually does not land in a crowded area. Area.
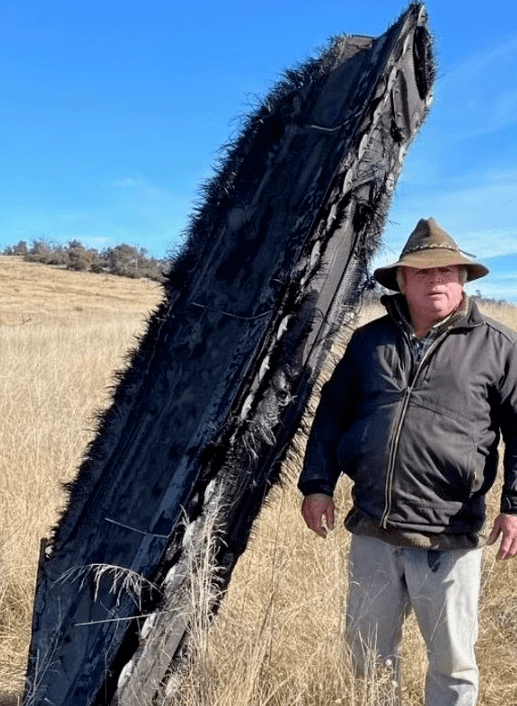
But there are always exceptions. For example, in March 2021, the wreckage of SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket fell on a farm in the United States.

Just a few days ago, a 3-meter-high wreckage of a giant spacecraft also fell from a farm in Australia. Finally, after investigation and verification, the wreckage came from the rocket of SpaceX’s Crew-1 mission.

The United States has previously made groundless accusations of “uncontrolled rocket wreckage” after the successful completion of my country’s Long March series rocket launch mission. In fact, so far in my country, there has not been a single incident of rocket wreckage falling into a crowded area. On the contrary, the United States It has happened repeatedly in recent years, and it is really a slap in the face!
So, what are the chances of rocket debris falling to the ground and hitting buildings or people on the ground?
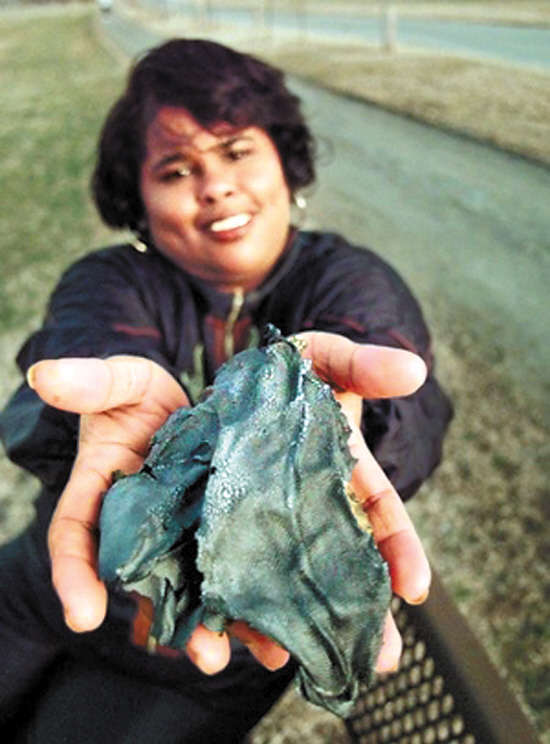
According to the available information, so far, only one person has been hit by space debris, which happened in 1997, when Lottie Williams, a resident of Tulsa, Oklahoma, was hit, But no fatal damage was done, and the fragment was about the size of a human hand.

Historically, some research institutions have analyzed the probability of space debris hitting people. Although the methods used are not the same and the results are not consistent, the overall results are about 1 in 10,000. However, this probability is the probability that the debris will hit any person anywhere on the earth, and if it is specific to each person, then the probability will be one in a trillion.
The calculation process is generally measured according to the distribution range and density of humans on the earth. As we all know, there are about 20% of the land on the earth, and most of the remaining oceans are by default considered to be devoid of human distribution. Then, on the land of the earth, only 20% of the area has human distribution, which means that after the space debris re-enters the atmosphere, there is a 4% chance that it will land in the area with human distribution.
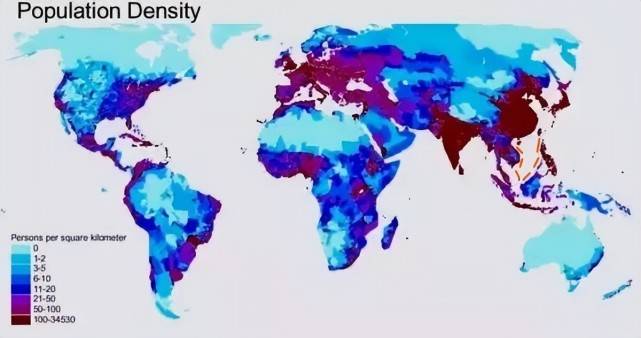
It seems that this probability is very high, but if we take into account the probability that space debris can reach the ground from its creation to the end, and then consider the proportion of inhabited land covered by humans, then in fact, the probability of space debris hitting people It will be greatly reduced on the basis of 4%, and it will drop to about 1/10,000 all of a sudden.

On the other hand, the possibility of space debris hitting various buildings or infrastructure, causing property damage, is much higher than hitting people. For example, if the space debris does not fall into the ocean, desert, forest, etc. In areas without human activities, hitting various roads, water conservancy facilities, houses, buildings, farmland, etc. will cause certain economic losses. After calculation, this probability is about 1%.



GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings